CARDIOLOGYZAGAZIG UNIVERSITY
- Home
- Links
- What's New?
- Staff
- Editors
- About us
- Cases
- Conferences
- Intnesive Cardiology Course
- Online Exam
- Contact us
- الأخبار
- الإستشارات
Echocardiography corner
Basic Echo
Part I: Steps of ECHO Exam
Prepared by Dr. Elsayed Farag, MD
Approach To Easy ECHO Exam
Patient.
Operator (? Analyzer).
Report.
Managing Doctor.
Echocardiographic examination protocol
Requirements:-
· Patient.
·Operator.
· Machine & Transducer.
Back ground Bases of exam.
Approach Sites.
Modes Used.
Sequences of Adult Doppler echo exam
Steps Sequences during Performing Doppler Echo exam.
Report.
I. Approach Sites:
(A) Standard Approaches:
- Parastenal: (Long axis, Short axis at different levels )
- Apical: (Ap 4ch, Ap 5ch, Ap 2ch)
- Subcostal:
(B) Other Approaches (when needed)
- Rt parasternal.
- Suprasternal.
- TEE.
II. Modes used for Examination:
- 2Ds
- M-mode
- Doppler (CFM, PW & CW,Tissue Dopp)
III.Sequences of Adult doppler echocardiographic examination
Assess Machine.
Assure Patient.
Hold & Manipulation Transducerand Perform whole Echo examination
Steps Sequences during Performing Doppler Echo exam.
Writing the report at end of examination
Assess Machine:
• Check (Date,keys, transducer).
• dentify patient name at beginning (picture & video recording).
Assure Patient:
• Clinical evaluation, (auscultation).
• Special positioning.
Hold Transducer:
• Holeded with thump on mark.
• Put on para-sternal area .
Steps during Performing Echo exam.
Displayed views on screen
Begin with Long Axis View.
With transducer in the same site Rotate transducer & proceed to Short Axis View at different levels.
Then change the transducer position to the Apical Approach and obtain Apical Views.
Notification (or Remomerization) of obtained. morphology & dimensions during examination.
For each echo view use all accessible specific modes. (2Ds, M-mode, PWD, CWD & CFM)
For each specific mode (2Ds, M-mode, PWD, CWD & CFM) 5-8 cardiac cycle should be spent for to judge the anatomy; physiology and pathology (more cycle examination is needed in abnormal vague pathology).
(1) displayed views on screen
Put Transducer on para-sternal area & observe the displayed views on screen:
a) Non displaying of any cardiac structure:
change to subcostal approach & check for:-
- Dextrocardia.
- Machine & transducer problem.
- Patient problem (Emphysema).
b)Appearance of any cardiac
structure
modify the displayed view by transducer adjustment, gain sitting &
proceed for completion of examination.
2) Begin Begin with Long
Axis view and study
the displayed 2Ds, M-mode, PWD, CFM of
all the structure.
(3) With transducer in same site proceed to short Axis at its different levels (GR.VS, MV, LV and apex) and study the displayed 2Ds, M-mode, PWD, CWD, CFM of different structures.
(4) Then change the transducer position to the apical approachand study the apical 4ch, 5ch and 2ch views (displayed 2Ds, PWD, CWD & CFM).
(5) Notification (or Remomerization) of pathology and measurement during examination.
LONG AXIS VIEW
|
Pericardium
(Anterior pericardium)
|
Upper
1/3 or 2/5
|
||
|
Rt.
Ventricular Anterior Wall
|
|||
|
Rt. Ventricular
Cavity ® RV Out Flow
|
|||
|
Intervintrecular
septum ® Anterior A.R
|
|||
|
Right1/4
|
Middle 1/4
|
Left 2/4
|
Lower
2/3 or 3/5
|
|
® LVOT
|
LVC
|
Lower
2/3 or 3/5
|
|
|
® AML
|
LVC ±
Ch.
|
||
|
® MVO
|
LVC
|
||
|
® PML
|
LVC ±
Ch
|
||
|
® base
of PML
|
LVPW (±
pm)
|
||
|
Pericardium
(Posterior pericardium
|
|||
SHORT AXIS VIEW
A- Short Axis Level of Great Vessels : (AV, PV, PA, )
Aortic valve (central).
RVOT (above).
PV & PA (right).
RA & TV (left).
LA (below).
IAS between LA & RA.
B- Short Axis at Level of MV
- Pericardium all around.
RV (wall & cavity).
Septum (basal septum).
LVcavity & wall with MV inside.
C- Short Axis at Level papillary Muscle.
- pericardium all around.
- RV (Wall & cavity) anteriorly and to LT.
- LV Septum (mid septum).
- LV cavity and wall with 2 papillary mus. (projection) at level of 4 & 7 o’clock.
D- Short Axis at Level of Apex:
- Pericardium all around.
- LV apex (wall & cavity).
APICAL FOUR CHAMPER VIEW
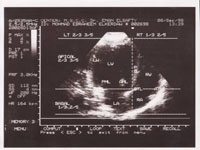
Apical 4 chamber view
Structure from apex to base:
·Pericardium all around
·Apex at Top
·IVS ® central cardiac body ® IAS (Dividing the view into left 3/5 or 2/3 and Right 2/5 or 1/3).
·Left 3/5 or 2/3: LV(Lateral wall & cavity), MV(Leaflets & opening), ® LA(cavity & wall with openings of pulm. veins).
·Rt 2/5 or 1/3: RV(Lat wall & cavity), TV(Ant & Sept. leflets & opening) ® RA (cavity & wall).
APICAL FIVE CHAMPER VIEW
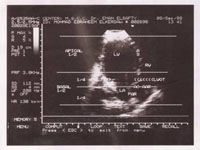
Apical 5 CH view
Part of Pericardium
Apical 2/3 - 3/5 :
(structure from apex to base and Lt. to Rt.)
·Apex at Top
·LV-post wall ® base of PML ® LA wall
·LVC ® MO & LVOT
·IVS (anterior septum)
·RVC
Apical 5 CH view (Continue)
Basal 1/3 - 2/5 :
(structure from apex to base and Lt. to Rt.)
·PML ® post. LA wall.
·MVO ® LA cavity.
·AML ® post AR.
·LVOT ® Aortic valve.
·IVS ® Ant. AR
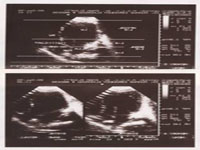
SUBCOSTAL VIEW
Subcostal View
• Sit-us (relation of IVC & AO to vertebrae).• Connections (Atria with ventricles & ventricles with great arteries)
• IAS.
• IVS.
• Valves.
• Chambers.
• Pericardium.
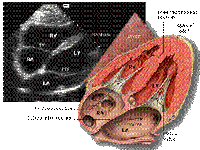
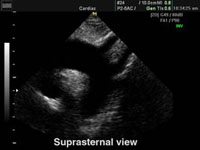
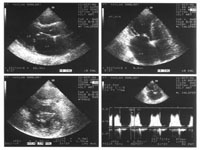
SUPRA-STERNAL View
S Suprasternal View
• Ascending Aorta.
• Aortic Arch.
• Branches of Aortic Arch.
• Upper part of Descending Aorta.
• Pulmonary Artery and branches.
DiDiagnostic for:
• PDA
• Ao.Co arctation.
• Ao. Aneurysm (& dissection).
• Others.